| Version 11 (modified by , 3 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
Google Summer of Code 2022
Introduction
So you are interested in becoming a Google Summer of Code student. What should you do to improve your chances of being selected? We recommend reading
- OSGeo's GSoC Recommendations for Students
- We currently some projects in mind listed below, with a mentor ready to help - refer to below. We are open to other ideas.
- Join the PostGIS Developers list and describe your proposed project (or willingness to work on Idea 1 listed below). We will let you know if we think the project is worthwhile and doable within the allotted time you have.
- If you are looking for additional ideas, refer to our past GSOCS:
Improving your chances
For most projects involving PostGIS you will eventually need the following:
- Know how to install PostgreSQL
- Know how to install PostGIS in PostgreSQL
- Know how to compile PostgreSQL code
- Know how to compile PostGIS code and run tests
- Some basic knowledge of git -- at least how to do a git clone, git push, git pull and pull requests
While you can learn to do these things and ask questions, we would prefer students to know these before starting on a PostGIS project.
Idea 1: Enhancing shp2pgsql / pgsql2shp to load/export topology elements and topogeoms
shp2pgsql is a commandline tool that is part of the PostGIS code base designed for loading ESRI shapefiles into a PostGIS database. pgsql2ship is a commandline tool that is used to export data into ESRI shapefile format.
Both tools currently only support geometry and geography formats. The plan is to augment them to support topology elements and topogeoms as well if the postgis_topology extension is installed.
Expected outcomes:
shp2pgsql will have new switches for loading into a topology. For topology elements, whether it loads into faces, edges, nodes will be dictated by the type of the data in the ESRI shapefile and will ignore the attribute data if any.
For topogeoms, the user would need to specify the table to create, topology, and column, with default column name being topo if the user does not specify. This will behave more or less the same as geography/geometry loading. For the first pass, we will assume this will just use basic topo element types (areal, lineal, punctal) and will not use subelements.
pgsql2shp will be used to export topogeoms and will use the topo::geometry casting to do so. Since topology tables faces, edges, and nodes are already tables, there is no need to support exporting topology.
Skills required:
Some familiarity with PostGIS, PostgreSQL, and postgis_topology Ability to compile PostGIS loader / dumper. Some familiarity with C.
Mentors: Regina Obe, Sandro Santilli
Difficulty: Medium
Idea 2: Augment pgAdmin to support importing and exporting shapefiles
Expected outcome: Import / Export Feature for Dbase and ESRI shapefiles:
1) There should be a menu option in the pgAdmin browser tree whenever you right-click a database, table, or schema that allows you to import or export Dbase/shapefiles. 2) The tool would use the shp2pgsql and pgsql2shp commandlines that are part of the PostGIS source code in much the same way the backup and restore data browse menu options built into pgAdmin utilizes pg_dump / pg_restore. It will look for the files in default runtime folder or user specified binary path.
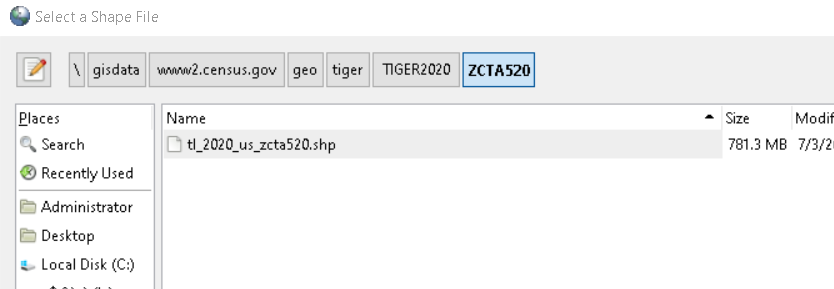
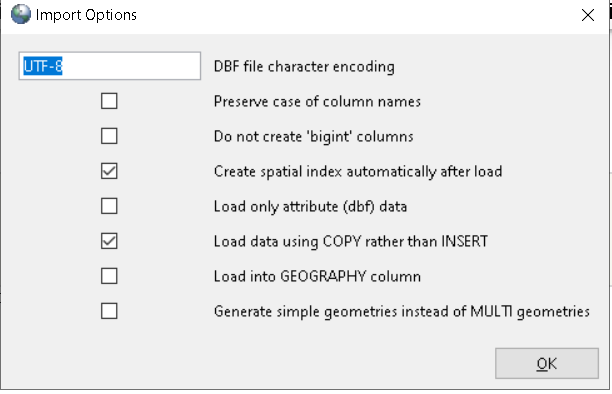
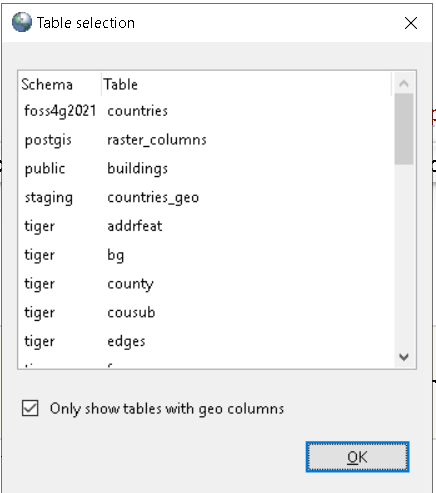
3) If a particular table is selected, it will give option to export as a Dbase/Shapefile or import (append to) (no need to ask for table aside from export/import path) or append to 4) If no table is selected - it will pop up a list of tables (as show in export screenshot) and allow user to import a file as a table in currently selected schema. If no schema is selected it would load in the default schema.
This is to replace in newer pgAdmin 4 6.5+ the shp2pgsql-gui plugin (which still exists but is standalone) that was hosted as a plugin in pgAdmin3. Here is a screen shot of what the old guis looks like. We want to achieve the same or similar functionality
Import
Export
Skills required:
python, html, css, and javascript, ability to compile pgAdmin
some familiarity with PostGIS, PostgreSQL, and pgAdmin is preferable
Ability to compile PostGIS and PostgreSQL code is a plus but not absolutely required.
Mentors: Regina Obe
Difficulty: Medium / Hard
Student Test:
- git clone code from PostgreSQL and compile
- git clone PostGIS code from one of Git repos and compile
- git clone code from pgAdmin4 and compile
- Create a working PostgreSQL database with postgis extension installed and shp2pgsql/pgsql2shp installed on system you are running pgAdmin4 on.
- Setup a public fork of pgAdmin repo for your work (can be osgeo, gitlab, github, or any other repo you can make available for public review)
Since the above is all work in pgAdmin, installing PostGIS / postgis commandline tools from a repository is equally acceptable to doing (1,2)
Attachments (5)
- postgis-qui-import-1.png (23.3 KB ) - added by 3 years ago.
- postgis-qui-import-2.png (23.0 KB ) - added by 3 years ago.
- postgis-qui-import-3.png (28.0 KB ) - added by 3 years ago.
- postgis-qui-export-1.png (18.7 KB ) - added by 3 years ago.
- postgis-qui-export-2.png (18.7 KB ) - added by 3 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip